
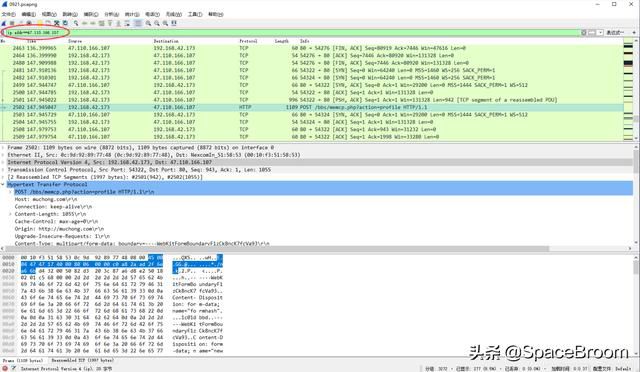
The ARP protocol was designed out of necessity to facilitate to translation of addresses between the second and third layers of the OSI model. Since this does involve a brief moment of connectivity loss, I do highly recommend letting the user of the target system know that you will be briefly disrupting their connectivity, especially if it is someone in management! This will put your sniffer and the target machine on the same broadcast domain and allow you to see all of the packets going to and from the target machine, as well as yours. Plug the targets network cable, along with the cable for your sniffer, into the hub, and then plug the hub into the network switch. Simply go to the switch that the target computer resides on and unplug it from the network. In order to do this, all you need is an old hub and a few network cables. Hubbing out is a technique in which you localize the target device and your analyzer system on the same network segment by plugging them directly in to a hub.

For instance, to capture the traffic of a device plugged in to port 3 on a switch, you could plug your sniffer into port 6 and enter a vendor specific mirroring command that mirrors port 3 to port 6. This is configurable by accessing the command line or GUI management for the switch the target and sniffer systems are plugged in to and entering commands which mirror the traffic of one port to another. Also called port spanning, this is a feature available on most managed network switches. Port Mirroring is probably one of the easiest ways to capture the traffic you are looking for. The goal of this article is to give a brief overview of port mirroring and hubbing out, which are very commonly used, and then to give a detailed explanation of ARP cache poisoning, the least well known of the trio.
The three most popular techniques for doing this are port mirroring, hubbing out, and ARP cache poisoning. Because of that we have had to come up with a few alternative techniques to getting the traffic we need. When you plug a sniffer in to a port on a switch, you can only see broadcast traffic and the traffic transmitted and received by your machine. As most of you know now however, the advent of switched networks prevents this. In the grand ole days of packet analysis when everybody used hubs you could plug in and sniff all of the traffic on a network segment. In fact, it is sometimes more difficult to place a packet sniffer on a network’s cabling system than it is to actually analyze the packets. Unfortunately, sniffing packets isn’t always as easy as plugging into an open port and firing up Wireshark.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
